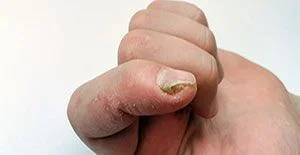
Condition Information
Fungus and yeast can infect the skin, nails, and hair. Fungal infections may be circular pink scaly patches on the skin, or scaling areas between the toes or in the groin. Fungally infected nails are usually yellow or white and thickened and crumbly. Some “laymen’s” terms that refer to fungal infections are “ringworm”, “jock itch”, and “athlete’s foot”. Yeast can become overgrown in moist areas of skin folds. Less commonly, there may be deeper fungal or yeast infections of the skin, which can look like crusted, inflamed, boggy, “pimply” areas on the skin. Usually, for these deeper infections, patients have an underlying predisposition for the infection, such as a suppressed immune system.
Treatment Information
The first step to treatment is identification and diagnosis of the fungal infection, as many other conditions can look similar to fungal infection. Topical antifungal creams and lotions are usually the first line of treatment for superficial infections. If these are ineffective or for deeper infection, oral antifungal medications such as Lamisil, Sporonox, Griseofulvin, ketoconazole, or fluconazole can be prescribed. Often, oral medication is needed to treat nail infections. Because most oral antifungal medications have side effects including damage to the liver, blood tests are generally used to monitor oral treatments. Fungal nail infection is not dangerous to the health, so a patient can choose if he or she wants to undergo oral treatment.